NB-IoT the ideal and low-power conection for IIoT
The NB-IoT or NarrowBand-IoT protocol is a protocol developed by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) for wireless communications, which is part of the LPWAN or Low Power Wide Area Networks.
NB-IoT is low power and narrow bandwidth, which, together with wide area operability and high-speed connections, have made it one of the main LPWAN standards of the 3GPP group. In addition, it is also a low-cost protocol with a high capacity to host a large number of devices, which is one of the main reasons why it is widely used in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), in public organizations and by users for personal use.
Although the protocol is called NB-IoT, it can also be considered a protocol to be used in industrial environments so it can be considered an IIoT protocol. The bands used in this standard vary depending on the region in which they are located, the available bands are the following:
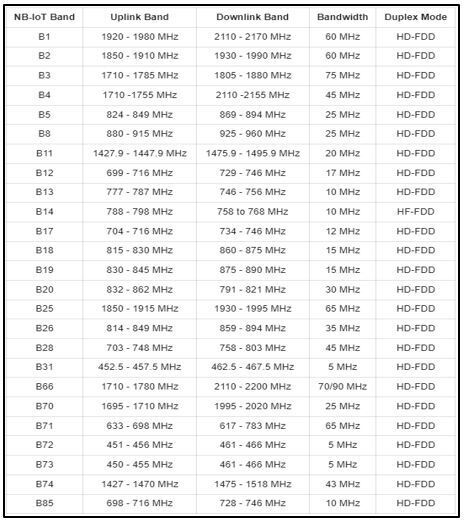
- NB-IoT Bands. Source -
Basic characteristics of the protocol
The most important features to highlight of this protocol are the following:
- Low power usage, so it does not consume a large amount of energy and the batteries can last for a long time.
- High bandwidth, which allows great connectivity to many devices.
- Wide area operation, which allows its use in areas of difficult access or rural areas where there is no good coverage.
- High communication speed.
- Low cost, therefore suitable for small businesses or personal use.
- Network encryption, which provides confidentiality and security against possible attacks.
- Easy integration into existing mobile systems.
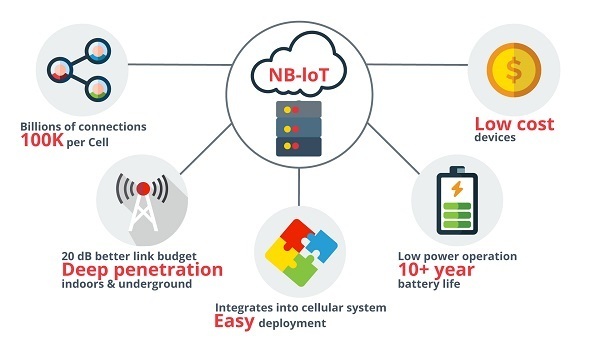
- Characteristics NB-IoT. -
Advantajes and disadvantajes
After knowing the characteristics of this protocol, it is convenient to know what its strengths and weaknesses are, in order to avoid any surprises in case of its use.
In addition to the previously mentioned advantages, the following characteristics can be found:
- High transmission in enclosed spaces or spaces insulated by different materials.
- Advanced management in the operating modes.
This has its disadvantages, which may include:
- High latency, up to several seconds, depending on the number of devices introduced.
- Low data rate, up to a maximum of KB.
- You cannot perform handshakes between repeater towers.
- Difficulty in over-the-air firmware implementation (FOTA).
- Lack of support for the mobility of the devices, so it is recommended that these be fixed.
Risk related to cybersecurity
As mentioned above, it is true that communications within the NB-IoT network are encrypted if so configured, but outside this, when navigating to the external server to which you want to connect there is no encryption, which is already a risk in itself.
The first risk encountered in this type of communication is to make an external connection as mentioned above. The second is that it is made through an unsecured connection or from an untrusted device. These two points are critical since an attacker can use various methods to compromise the security of the network, such as a man-in-the-middle to obtain the information being shared.
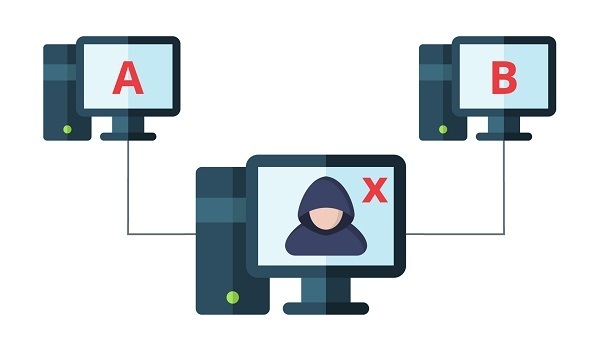
- Man-in-the-middle. -
A third risk is that with this man-in-the-middle attackers can introduce false information into the NB-IoT network, compromise the software by means of attacks on the firmware or attacks on vulnerabilities in the devices that have been discovered in the communication, etc. Therefore, care must be taken when making connections to servers and following certain guidelines that will be explained in the following section.
Security requirements
Minimum security requirements must be implemented to ensure that the devices are secure as soon as the device is installed, these requirements are as follows:
- Capability to implement the latest firmware version in the different installed devices.
- Capability to install a SIM card.
- Certificates and passwords should be stored on the SIM card ensuring a high level of security.
- SIM cards must have an unalterable identification number (ICCID) stored in its memory, which is read-only.
- A tunnelling protocol, such as Layer Two Tunnelling Protocol (L2TP), or a secure protocol, such as Internet Protocol Security (IPSec), should be used to create a VPN.
- Secure access control should be implemented by setting up secure passwords.
- Protect hardware components against possible tampering or memory extraction. An example would be the use of hardware security chips or the implementation of security seals on the devices themselves to prevent tampering.
As for the network, there are also certain minimum-security requirements that must be implemented:
- Ensure the use of the latest version of the standard for the devices on the network.
- ICCID control to avoid possible SIM card spoofing or duplication.
- Establish strong access control policies, either through firewalls or other security devices to filter unwanted traffic.
- Resilience to possible hardware failures or attacks.
- Security at the physical layer of the network, this means protecting base stations and infrastructure components against physical intrusions.
Solutions and mitigations
At this point, certain methods can be found to minimize the risks previously mentioned, the guidelines to be followed are the following:
- Keep network exposure to a minimum.
- Reduce the range of the network to the physical environment, either by software or by placing hardware that reduces the signal level.
- Make connections through encrypted systems such as proprietary VPNs or provider APNs.
- Some providers offer an intermediate server within the network, which collects the data and sends it via a VPN connection to the server.
- This provides a high level of communication security but implies additional costs for the customer and little flexibility to operator changes.
- Some providers offer an intermediate server within the network, which collects the data and sends it via a VPN connection to the server.
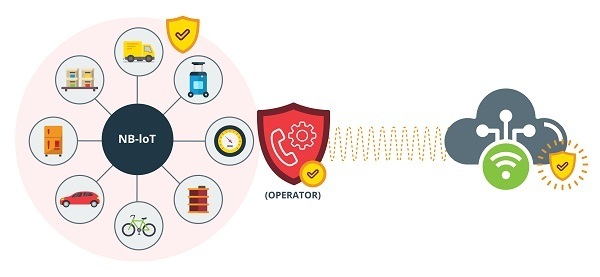
- Use of provider VPN. Source -
- UDP protocol security.
- Data will travel end-to-end encrypted by the same technology.
- This will allow a high level of network security and user independence from an operator but will increase the development time of the solution.
- Data will travel end-to-end encrypted by the same technology.
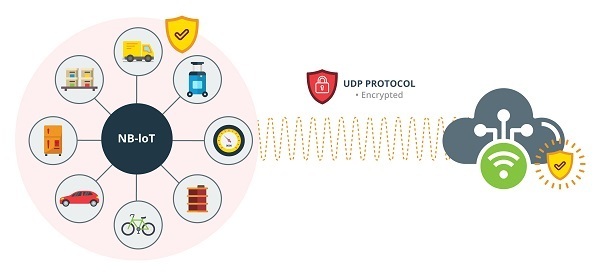
- UDP protocol securization. Source -
- Traffic control within the network by means of IDS or IPS software.
- Software update of the different devices that make up the NB-IoT network.
- Hardware elements that protect the installation, an example of which would be a firewall, which would detect unauthorized communications or access.
Conclusion
The NB-IoT protocol can be a viable protocol for companies or individual users with access difficulties either by geological or financial means. This protocol provides great advantages, although the use of this protocol must be considered because the drawbacks can cause great losses. It is also important to mention that communications must be secured in the best possible way to minimize the risk of attack.









