Maximising security in the cloud: the essential role of CASB

With the rise and widespread adoption of cloud-based solutions, information security has taken on unprecedented relevance. Organizations, regardless of size or industry, are in a constant race to protect their digital assets, in an environment where threats evolve with technology. The growing dependence on cloud services has multiplied the points of vulnerability, opening doors to possible exposures that can compromise not only the integrity of the data, but also the reputation and operability of the organization. In 2023, 39% of companies suffered some type of cloud-related data breach.
It is not just malicious actions by cybercriminals that pose a risk, inadvertent employee errors, natural disasters, device or application failures, and internal sabotage also pose significant threats. Security in cloud environments is so important that the latest update of ISO 27001 in 2022, in its annex A 5.23, already establishes a specific control to address information security in the use of cloud services. Its purpose is to ensure that organizations properly specify and manage information security for the use of cloud services. According to the definition of ISO 27001:2022 annex A 5.23, 'the processes for the acquisition, use, management and exit of cloud services should be established in accordance with the information security requirements of the organization'.
In this context, it is essential to have tools and protocols that ensure adequate security management in cloud environments. This emphasis reinforces the need for solutions that enable organizations to meet these standards while benefiting from the flexibility and scalability that the cloud can offer.
In the current technological landscape, cloud access security systems, known as CASB (Cloud Access Security Broker), emerge as a key solution, which serves as a link between the local infrastructure of companies and cloud services, operating as controllers of security measures that are located between corporate users and providers of these services. In addition to providing essential control and visibility to protect sensitive data through all stages of the information flow, CASB integrate a variety of security strategies. These range from validation and granting of permissions to encryption and detection of malicious software, regardless of whether devices are monitored or not.
Advantages offered by CASB
The adoption of CASB solutions provides a variety of advantages that enhance the cloud security strategy of organizations. Below are the most prominent advantages:
- Real-time policy enforcement: CASB allow organizations to enforce security and compliance policies in real time, ensuring that all data flowing to and from the cloud is subject to rules set by the company. This capability helps sensitive data to be handled in accordance with corporate guidelines and relevant regulations, avoiding IT Shadow practices.
- Real-time policy enforcement: CASB allow organizations to enforce security and compliance policies in real time, ensuring that all data flowing to and from the cloud is subject to rules set by the company. This capability helps sensitive data to be handled in accordance with corporate guidelines and relevant regulations, avoiding IT Shadow practices.
- Improved and unified visibility in the cloud: one of the biggest challenges for companies in the cloud space is the lack of visibility into their data and applications. CASB provide a unified view of all cloud resources and activities, allowing security administrators and architects to track, monitor, and control which applications can be accessed by their employees, especially distinguishing between sanctioned (officially approved by the organization) and non-sanctioned applications. This is very useful when managing multicloud services with different providers.
- Simplified regulatory compliance: with the appearance and updating of regulations such as ISO 27001 – already mentioned above – and the National Security Scheme – which has recently incorporated a specific profile for the cloud environment also in 2022 – added to the crucial attention on data protection dictated by the LOPDGDD, it becomes imperative that organizations demonstrate their commitment and actions to safeguard information. In this scenario, CASB emerge as valuable tools, providing companies with media and records that allow them not only to maintain, but also to accredit, their adherence to current regulations and standards.
- Mitigation of risks associated with unsupervised devices: in the era of BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) many employees access company resources from personal devices. CASB ensure that, even in these scenarios, cloud data is protected by enforcing security policies, regardless of the device used.
Operation
The CASB typically applies the following functions to manage corporate data in the cloud that can be accessed by authorized and unauthorized applications. First, it performs identification, in which it detects all cloud applications in use and related employees. Subsequently, it enters the evaluation phase, where each application is analyzed, recognizing its data, and estimating a risk index. Finally, in the mitigation stage, a custom policy is configured for the entity based on its security requirements, allowing the CASB to detect and neutralize any emerging hazards or breaches.
In terms of implementation, CASB stand out for their simplicity in integration and management. There are three main deployment modes for CASB and while most are installed in the cloud, there are also alternatives for on-premises deployments.
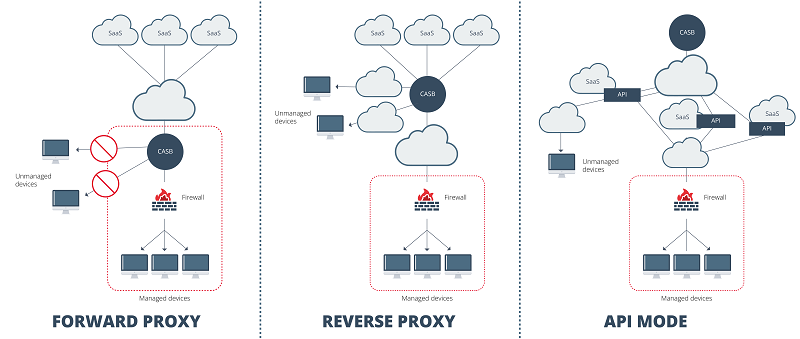
- Basic modes of operation of CASB -
The following details the deployment, client configuration, control, and use of these deployment methods:
| Forward proxy | Reverse proxy | API Mode | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deployment | The forward proxy is placed between the end user and the Internet. This means that all user traffic first passes through the CASB before reaching the cloud service. | The reverse proxy sits between the Internet and the cloud service. Unlike the Forward Proxy, it does not require any configuration on the user's device. | API mode does not act as a proxy between the user and the cloud service. Instead, it integrates directly with the cloud service's API, allowing you to inspect and control data at rest within the application. |
| Client configuration | Requires configuration on end user devices. This can be problematic for unmanaged or BYOD devices, as organizations do not have direct control over these devices. | It requires no configuration on users' devices. Users are redirected through the CASB using techniques such as URL rewriting. | It does not require any configuration on the client side, as it does not interfere with real-time traffic between the user and the cloud service. |
| Control | You can control traffic to authorized and unauthorized applications because all traffic passes through the proxy. | Generally, it is limited to specific or authorized applications, as it depends on the integration between the CASB and the specific application in the cloud. | Its control is mainly focused on data at rest. You can perform functions such as data classification, sensitive content detection, and implementation of access control policies based on specific data. However, it does not inspect or control traffic in real time. |
| Use | It is especially useful in scenarios where organizations want to control which cloud services can be accessed and which cannot. | It is ideal for organizations that use specific cloud applications (such as Office 365 or Salesforce) and want granular control and visibility over those applications. | API mode is particularly useful for scenarios where organizations want to inspect content stored in cloud applications (such as storage or collaboration services) and enforce security and access control policies without impacting the real-time user experience. |
CASB in proxy mode offer flexibility when interacting directly with data, fitting almost any SaaS application. Despite this, they face challenges such as performance by acting as an intermediary and the management of TLS sessions, which can be interrupted by the CASB, assigning it typical security tasks of a browser. This intervention can complicate safety decisions.
On the other hand, API-based CASB bring security to SaaS using their own connection interface. They have no issues with TLS like in proxy mode, but their scope may be limited due to SaaS-specific APIs. It is crucial for infrastructure architects to determine which SaaS applications they want to support before settling on a solution. Multimodal CASB leverage all of these modes of operation to provide optimal adaptability.
Applications
As for its practical applications, CASB offer a set of fundamental tools aimed at securing and efficiently managing data in cloud environments, being very useful for professionals such as network and system administrators and security architects. These applications focus on different aspects of data flow and access to cloud services. Below are some of the main applications of CASB systems:
- Cloud traffic monitoring and control: CASB allow you to monitor traffic between users and cloud services. This capability is critical for detecting anomalous patterns of behavior, such as access to unusual schedules or bulky data transfers, which could indicate a leak or security breach.
- Data Leak Prevention (DLP): wth the increasing amount of data stored in the cloud, leak prevention has become a priority for many organizations. CASB integrate DLP tools that identify and block the unauthorized transfer of sensitive or confidential data.
- SaaS Vendor Assessment: before adopting any cloud service or application, it is essential to assess the vendor's security. CASB can gain information from applications that can help organizations evaluate and compare different vendors, ensuring they meet the necessary security standards.
- Data encryption: it is essential to ensure that data is secure when stored or transmitted. CASB offer encryption solutions for data in transit and at rest, ensuring sensitive information is protected at all times.
Conclusion
Information protection is not only a technical necessity, but an essential component in the constant evolution and improvement of any modern organization. Information, especially sensitive data, is one of the most valuable assets of any entity. Exposing this data due to lack of adequate security measures can lead to legal, economic and image consequences.
CASB solutions are critical to safeguarding information, and when complemented with other systems, such as backups and continuity plans, resilience and protection are strengthened. These tools are not only critical to data assurance, but also allow organizations to enjoy the benefits of the cloud, such as scalability and flexibility, without compromising their integrity and security. In addition, these strategies align companies with regulations and compliance with the law.









